A
Active Learning: An instructional method that engages students in the learning process through activities and discussions.
API (Application Programming Interface): A set of protocols and tools for building software applications, allowing them to communicate with each other.
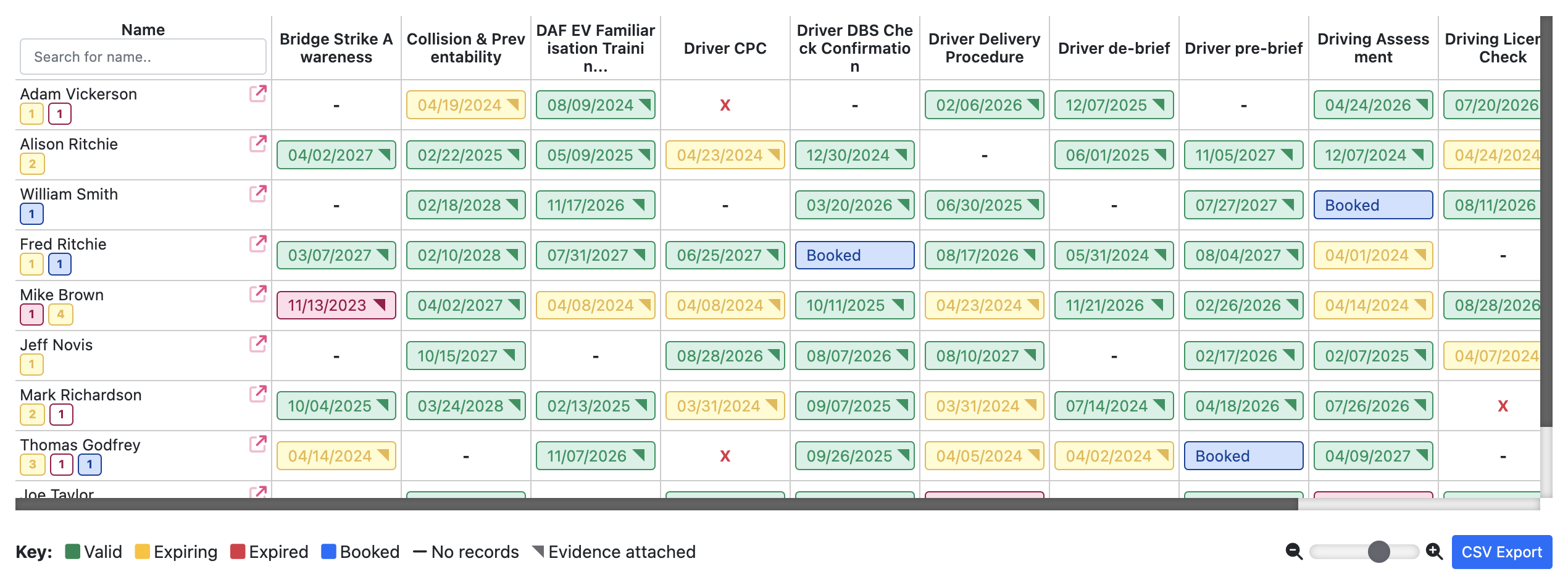
Automated Training Matrix: A tool providing a real-time visual overview of training compliance and gaps, streamlining the management of training records and compliance status.
B
Blended Learning: A training approach that combines online digital media with traditional face-to-face methods.
BYOD (Bring Your Own Device): A policy allowing employees to use their personal devices for work purposes, accessing the company’s network and resources.
C
Certificate Storage: A feature for the secure storage and easy retrieval of training certificates and records.
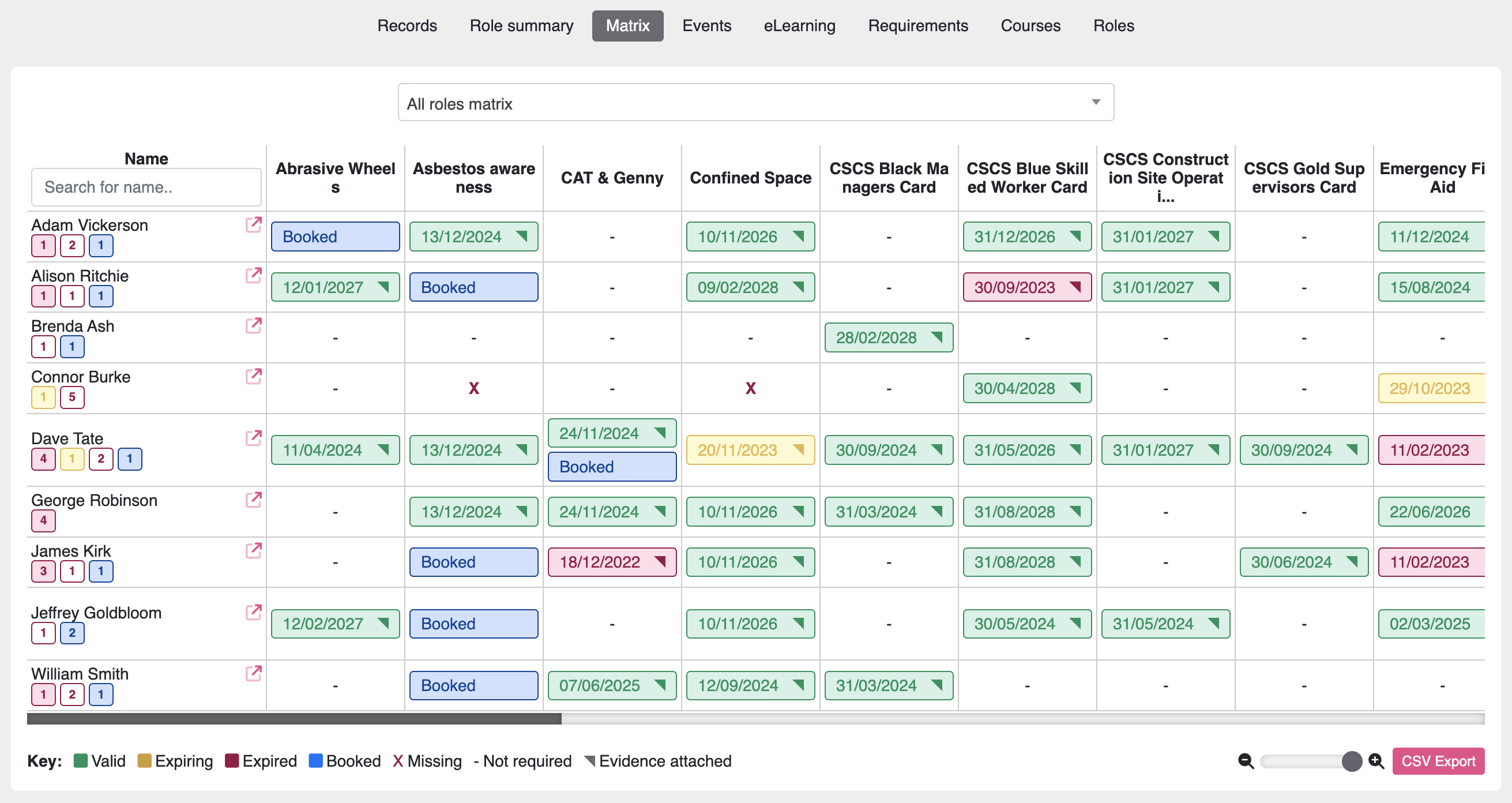
Competency Matrix: A table mapping the skills, knowledge, and behaviours required for different roles against the current competencies of team members, helping identify strengths and areas for development.
Compliance Training: Training programmes designed to educate employees on laws, regulations, and company policies applicable to their job function or industry.
Corporate Training: Training programmes designed to improve the skills, knowledge, and performance of employees within an organisation.
D
Data Analytics: The process of examining data sets to draw conclusions about the information they contain, often using specialised systems and software.
Distance Learning: A method of studying where the instruction is carried out over the Internet, rather than in a traditional classroom setting.
E
eLearning: Learning conducted via electronic media, typically on the Internet, providing flexibility and accessibility to learners.
Email Reminders and Alerts: Automated notifications sent via email to remind users of upcoming training needs, renewals, or other important deadlines.
F
Formative Assessment: Ongoing assessments used to monitor student learning and provide continuous feedback to improve instruction and learning outcomes.
G
Gamification: The use of game design elements and principles in non-game contexts to engage users and enhance their learning experience.
H
Hybrid Learning: An educational approach that blends online and in-person learning activities, providing flexibility and access to resources both in the classroom and online.
I
Intelligent Dashboards: Interactive displays providing an overview of key metrics and performance indicators, helping users quickly identify problem areas and monitor progress.
Instructional Design: The practice of creating educational resources and experiences in a systematic and efficient manner to enhance learning and performance.
J
Just-in-Time Learning: An approach where learners access the information they need at the moment they need it, facilitating immediate application of knowledge.
K
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Metrics used to evaluate the success of an organisation, employee, or project in meeting objectives for performance.
L
Learning Management System (LMS): Software used to create, administer, track, and report on educational courses and training programmes.
Learning Path: A sequence of courses and learning activities leading to mastery of a particular topic or set of skills.
M
Medical Monitoring: Tracking and managing employee health assessments and screenings, such as tests for drug and alcohol use, exposure to harmful substances, and other health-related evaluations.
N
NDA (Non-Disclosure Agreement): A legal contract establishing a confidential relationship between parties to protect sensitive information.
O
Onboarding: The process of integrating a new employee into an organisation and familiarising them with its policies, procedures, and culture.
P
Professional Development: Training and education activities that help individuals improve their skills and knowledge within their professional field.
Proficiency Levels: Stages of skill development that employees can achieve, typically categorised as beginner, intermediate, advanced, and expert.
R
Return on Investment (ROI): A measure used to evaluate the efficiency or profitability of an investment, comparing the amount of return to the investment’s cost.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): A system that restricts access to authorised users based on their role within an organisation, enhancing security and data management.
S
SCORM (Sharable Content Object Reference Model): A set of technical standards for eLearning software products to ensure they work together seamlessly.
Skills Matrix: A visual representation of the skills and knowledge of employees, helping organisations identify training needs, track development, and ensure employees are qualified for their roles. See the Moralbox skills matrix software.
Software as a Service (SaaS): A software distribution model where applications are hosted by a service provider and made available to customers over the Internet.
Succession Planning: The process of identifying and developing internal personnel to fill key leadership positions within an organisation.
Summative Assessment: Evaluations conducted at the end of an instructional period to measure student learning, skill acquisition, and academic achievement.
T
Training Needs Analysis (TNA): A strategic process used to identify and address gaps between current employee skills and those required for effective job performance.
Training Matrix: A tool used to track and manage training requirements and completion statuses for employees, often visualised in a grid format. See the Moralbox training matrix software.
Training Profiles: Individual records detailing the training history, certifications, and skill assessments of each employee.
Training Management System (TMS): Software that automates the administration, tracking, and reporting of training programmes.
U
User Experience (UX): The overall experience of a person using a product, especially in terms of how easy and pleasant it is to use.
V
Virtual Classroom: An online learning environment that allows for live interaction between the instructor and learners.
Virtual Reality (VR): A simulated experience that can be similar to or completely different from the real world, often used for training and educational purposes.
W
Webinar: A seminar conducted over the Internet, allowing participants to interact and engage with the presenter in real-time.
Work-Based Learning: Learning that occurs within a work context, utilising the employer’s resources and environment for practical training.
Workforce Manager: A comprehensive tool that helps organisations manage training, compliance, and employee development in a centralised and efficient manner.